Why It’s Important
home
Residential Program
Commercial Program
Government & Public Entities Program
Sponsors
Lawn and Garden Equipment in Colorado
Substantiating the significance of Lawn and Garden equipment to our air pollution challenges, the State of California found that 84% of small, off-road engines were for lawn and garden care.
There are more small engines in California (16.7 million) than there are light-duty passenger cars (13.7 million) !
These small engines are mainly lawn and garden equipment! 77% residential lawn and garden equipment, 9% commercial lawn and garden equipment, 11% federally regulated construction/farming equipment, and 3% other equipment types (e.g., generators, utility carts).
(PDF) Sources of Ozone-Causing Pollution in Tons per Day (TPD) – Data with small chart (7)
In 2018, 35% of Colorado’s “non-highway use of gasoline” was for the Lawn and Garden sector. Lawn and Garden is by far the largest consumer of gasoline in this “non-highway” group, which includes recreational vehicles, agricultural, and construction.
https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/policyinformation/statistics/2018/mf24.cfm
Emissions Reductions from Replacing Gasoline-Powered Mowers with Electric-Powered Mowers
These figures are for our residential program, assuming 1 hour per week of lawn mower use.
Ozone Precursors – Sources of the Chemical Reaction that Produces Ozone Pollution
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):
0.234 lbs./year x 1,000 mowers = 234 lbs./year / 2,000 lbs. = .117 tons/year
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC):
2.28 lbs./year x 1,000 mowers = 2280 lbs./year / 2,000 lbs. = 1.14 tons/year
Combustion By-Products – Result of Burning Gasoline
Carbon Monoxide (CO):
26 lbs./year x 1,000 mowers = 26000 lbs./year / 2,000 lbs. = 13 tons/year
Greenhouse Gasses (CO2 eq.):
490 lbs./year x 1,000 mowers = 490,000 lbs./year / 2,000 lbs. = 245 tons/year
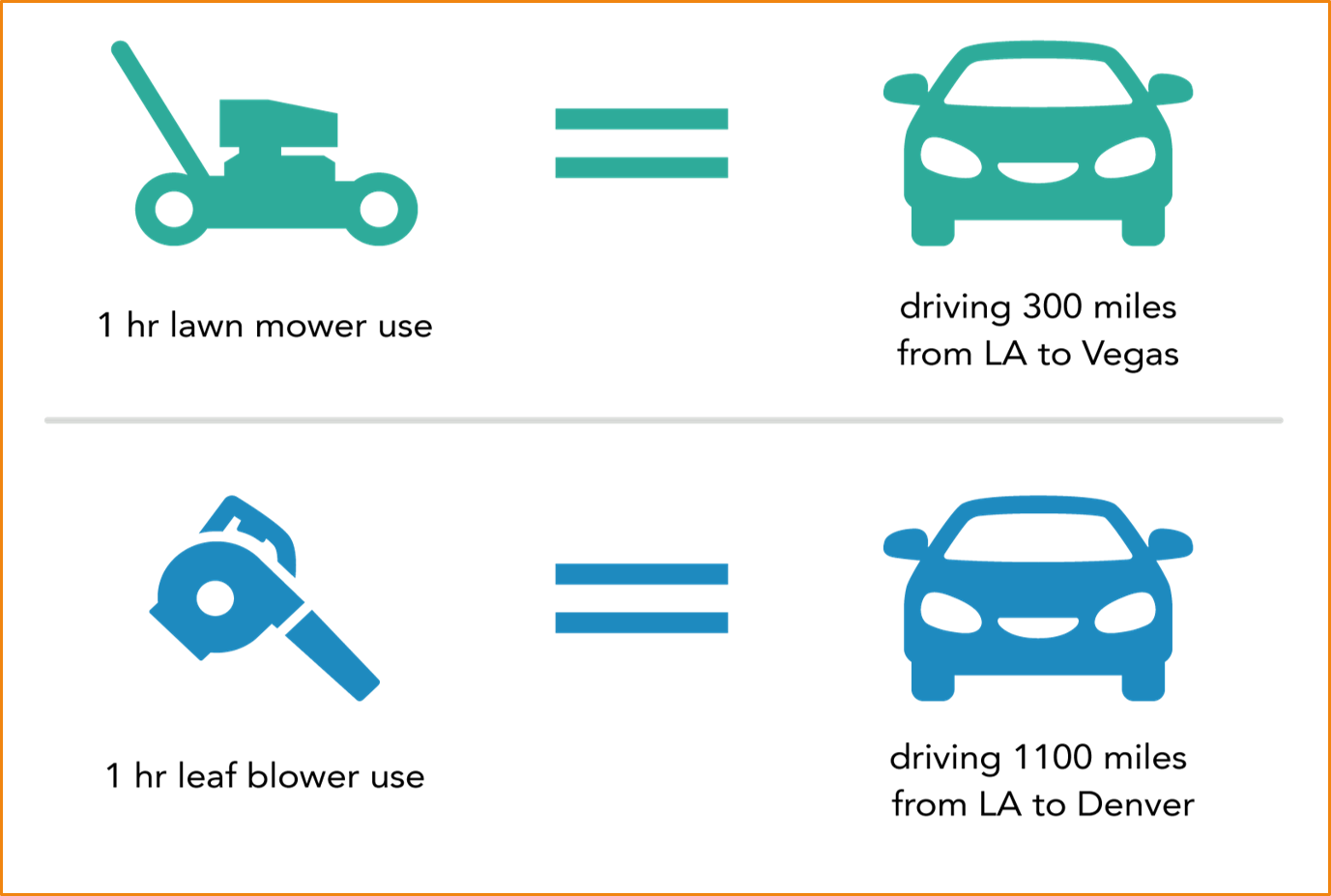
Car Pollution and Pollution From Lawn and Garden Equipment